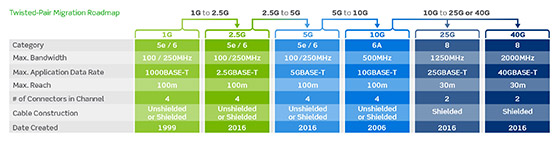
Get pro tips and recommendations for installing Cat.6AOver the past five years, Cat.6A adoption has increased dramatically, becoming the dominant media type for 10 Gb/s networks. Hospitals, schools, and other enterprise networks applications like wireless and power over Ethernet all rely on Cat.6A cabling for greater bandwidth to meet today's data demand. And when comparing costs per port of equipment, maintenance, and assembly of 10G Ethernet, Cat.6A with twisted pair has become significantly more costeffective than other technologies.
Cat.6A cables are larger and heavier than Cat.6 or 5e cables and may require some different routing and handling techniques. Leviton's Cat.6A Interactive Guide gives you a better understanding of these requirements to more efficiently plan, bid, and install a Cat.6A system. |
|||

|
|||
|
Leviton Contact us CASL | Privacy | Accessibility |Unsubscribe If you visit any links we will provide your subscription contact info (not your email) to the advertiser or sponsor. Copyright ©yyyy Annex Business Media P.O. Box 530, 105 Donly Drive S, Simcoe, ON, CANADA N3Y 4N5 customercare@annexbusinessmedia.com Customer Service: Tel 1-800-668-2374 |